SAM 3D, Meta’s latest vision model, does something most AI tools still struggle with: it understands an image well enough to reconstruct it in 3D.
Paired with SAM 3, which detects and tracks objects across pictures and videos, it moves visual AI from content filters into technical-grade interpretation.
That matters because once AI sees structure, not just style, it stops being a design assistant and starts becoming an operational tool.
So what?
AI is crossing from making visuals to understanding them.
What changes and why it matters
Until now, most visual AI models have focused on generating or touching up images. SAM 3 and SAM 3D reverse that logic. They are built to detect, segment and reconstruct what already exists. This lowers the barrier to advanced image editing, technical inspection and basic 3D modelling.
For creators, that means faster visual production without complex tools. For engineers, it introduces structured image analysis. For robotics, it improves how models understand physical space.
So what?
The value shifts from image quality to image comprehension.
Core capabilities
Detection — SAM 3
SAM 3 is designed to recognise and isolate objects in images and video, even in scenes with visual noise, partial obstruction or overlapping subjects
The model operates at the frame level and across motion, enabling it to track how specific items move over time without requiring manual bounding boxes.
This allows precise editing, targeted visual effects, and reliable object isolation in inspection or surveillance footage.
In early demonstrations, SAM 3 consistently separated foreground subjects from cluttered backgrounds with only image prompts, without retraining.
It performs exceptionally well on general-purpose scenes and is trained to adapt to different lighting conditions and camera types, making it practical for real-world visuals rather than studio-grade material.
Reconstruction — SAM 3D
Builds a 3D model from a single image. Useful for concept validation, spatial reasoning and simulations.
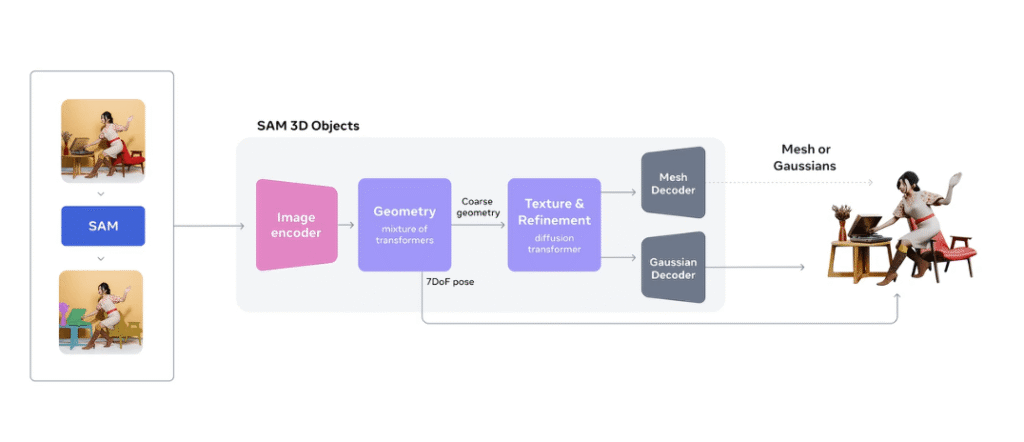
SAM 3D is actually a pair of foundation models rather than one single system. SAM 3D Objects focuses on general scenes and items. It reconstructs the entire 3D geometry, texture, and layout from a single image and is built to handle clutter, occlusion, and real-world mess rather than clean studio shots. SAM 3D Body focuses on humans.
It estimates 3D pose and body shape from a single photo and uses a new Meta Momentum Human Rig format to separate the skeleton from soft tissue. Hence, the results are easier to interpret and reuse. Both models are trained at a large scale and achieve state-of-the-art performance on in-the-wild 3D reconstruction benchmarks.
Meta has released the SAM 3D Objects and SAM 3D Body checkpoints, code and an online demo under its SAM license, along with a new benchmark dataset for 3D reconstruction in natural scenes. In human preference tests on real objects and scenes, SAM 3D Objects outperforms earlier leading models by at least 5-to-1, confirming that visual quality is not just a lab claim but measurable in side-by-side comparisons.
Accessibility
Meta made both SAM 3 and SAM 3D available through the Segment Anything Playground, allowing users to upload their own images and test segmentation or 3D reconstruction without coding.
Advanced users can interact with the models via Python or API hooks, and the standard release includes integration examples for image editing tools and pipeline automation.
Because the models are open under Meta’s license, developers and researchers can adapt them to domain-specific use cases, including visual editing, inspection automation and training dataset enrichment.
What this looks like in practice
Imagine a drone image of solar panels on a rooftop. SAM 3 highlights each panel, traces boundaries and flags misalignments. Feed the image into SAM 3D, and it generates a basic 3D structure that can support layout decisions or proposal documentation.
A creator isolates a moving subject in video footage without manual tracking. A robotics engineer uses a single image to approximate spatial depth. A filmmaker blocks a scene from a still photograph.
Meta is already using SAM 3 and SAM 3D inside its own products. In the Edits video app, SAM 3 will soon power effects that apply only to a specific person or object in a clip. On Facebook Marketplace, SAM 3D drives a View in Room feature that lets people drop a reconstructed table or lamp into their living space before they buy.
The company also plans to bring SAM-powered creation tools into the Vibes experience in the Meta AI app, and highlights research use cases in robotics, science and sports medicine.
So what?
AI now interprets usable spatial context from visuals that once required on-site inspection or manual processing.
How to test it
- Use Meta’s Segment Anything Playground for quick experiments.
- Export segmentation maps into editing or modelling tools.
- Combine with drone or camera footage to pre-screen faults or layout issues.
- Integrate outputs into reporting or prototyping workflows.
Start with one image of a task you typically explain manually. Ask SAM to isolate or reconstruct it. If it removes a step, you found your use case.
Objections and limitations
- Privacy risk: People can extract object details from photos without consent.
- Accuracy: 3D outputs are approximations, not engineering-grade models.
- Power demand: High-resolution use may depend on cloud access.
- Environment constraints: Performance can drop in low visibility, with older camera hardware, or with non-standard spatial layouts.
- Bandwidth: Not ideal for regions with unstable connectivity unless adapted for edge devices.
So what?
Treat it as a first pass, not a final model.
Where to apply now
If you work in:
Content and Media Applications
SAM 3 allows creators to isolate subjects in images and videos without manual masking or frame-by-frame selection.
This simplifies tasks such as background removal, scene compositing, and visual effects work. Content editors can automatically track movement and apply changes to a person or object across an entire sequence.
Combined with SAM 3D, a single photo can be turned into a basic 3D reference to support shot planning or concept visualisation. Whether used in marketing, broadcasting or digital storytelling, these models reduce production effort and make advanced editing tools accessible to smaller teams and independent creators.
Inspection and Technical Use Cases
In inspection workflows, SAM 3 can segment structural elements, surfaces or equipment directly from camera or drone footage.
This helps teams quickly identify defects, alignment issues or signs of wear without manually reviewing every frame. Using SAM 3D, visual data can be reconstructed into an approximate spatial model that supports documentation, layout assessment or pre-visit planning.
These capabilities are valuable in sectors such as energy, construction and facility management, where visual analysis is often performed onsite. AI-assisted segmentation offers faster initial assessment, although final validation still requires professional evaluation.
Robotics and Spatial Intelligence
In robotics, combining object detection and 3D reconstruction enables better spatial reasoning with standard cameras. SAM 3 helps systems recognise items in cluttered or dynamic environments, while SAM 3D approximates depth and orientation from a single perspective.
This supports object interaction, basic navigation and environmental understanding without relying solely on specialised sensors.
Although early-stage, these models enable robotics platforms to begin operating in semi-structured environments such as homes, retail settings or small-scale industrial spaces where traditional mapping systems may struggle.
Education and Demonstration Systems
SAM 3 and SAM 3D enable converting everyday images into teaching visuals and simplified technical illustrations. Educators can highlight components within a photo or generate approximate 3D interpretations to explain how a system works.
This lowers reliance on complex modelling software when preparing training materials or presentations. The models are beneficial for visually communicating concepts in engineering, healthcare, design, and vocational learning.
While not suited to precision technical design, they provide a fast and effective way to demonstrate ideas, especially during early understanding or concept clarification.
Final thought
Visual AI is moving from imagination to interpretation. SAM 3 and SAM 3D mark the moment when machines begin to see context, not just pixels. The question is no longer whether image AI will be beneficial, but whether you will integrate it before competitors do.
If you already capture images, you are halfway there. The next step is asking AI what it can see that you cannot.